Discover how JP Morgan grew from a 19th-century investment bank into a global financial leader. Learn about its history, mergers, global expansion, core services, tech innovation, and role in shaping modern finance across 100+ countries.
Discover how JP Morgan grew from a 19th-century investment bank into a global financial leader. Learn about its history, mergers, global expansion, core services, tech innovation, and role in shaping modern finance across 100+ countries.
Image courtesy of Dezeen
J.P. Morgan, the investment banking and financial services division of JPMorgan Chase & Co., stands as one of the most influential institutions in global finance. With a history spanning over 150 years, J.P. Morgan has built a reputation for innovation, trust, and stability across the world’s financial markets. Today, it plays a central role in driving economic growth and connecting capital to ideas globally.
JPMorgan Chase & Co. is a multinational financial services firm and the largest bank in the United States by total assets, market capitalization, and revenue. It operates at the heart of global finance, offering an extensive range of services from investment banking and commercial banking to wealth management and transaction processing.
J.P. Morgan (part of JPMorgan Chase & Co.).Founded: 1871 (as Drexel, Morgan & Co.). Founder: John Pierpont Morgan. Headquarters: New York City, USA. Parent Company: JPMorgan Chase & Co. Global Presence: Operations in over 100 countries. CEO of JPMorgan Chase: Jamie Dimon (since 2005)
JPMorgan Chase’s lineage is complex, shaped by a series of historic mergers, acquisitions, and banking milestones. Its roots trace back to several legendary financial institutions, the most notable being:
Established by the famed financier John Pierpont Morgan, it became one of the most influential banking houses in U.S. history. J.P. Morgan helped finance major industries such as railroads, U.S. Steel, and General Electric, and even stabilized financial markets during the Panic of 1907.
Founded in 1799 as the Bank of The Manhattan Company, it merged with Chase National Bank in 1955 to become Chase Manhattan. It was known for commercial and consumer banking.
Chemical Bank and Manufacturers Hanover: Both major New York banks that merged in the 1990s, eventually combining with Chase Manhattan.
Bank One Corporation (2004): A crucial acquisition that brought Jamie Dimon, the current CEO, into JPMorgan Chase. This merger added strong credit card, retail banking, and middle-market capabilities.
These institutions combined to form the modern JPMorgan Chase & Co., officially established in 2000 following the merger of Chase Manhattan Bank and J.P. Morgan & Co.
Founder: John Pierpont Morgan (J.P. Morgan). Born: April 17, 1837, Hartford, Connecticut. Died: March 31, 1913, Rome, Italy. Son of Junius Spencer Morgan, an American banker who had already established strong banking ties in London with the firm George Peabody & Co., which later became J.S. Morgan & Co.
Timeline of the Founding and Evolution of J.P. Morgan & Co.
Early Banking Roots (1854–1870s)
1854–1860s: J.P. Morgan trained in finance in Europe, especially London and Paris.
1860: Morgan returned to the U.S. and began working with Duncan, Sherman & Company, the American representative of his father's bank.
The Start of J.P. Morgan’s Independent Banking Career
1864: Morgan founded his first firm, Drexel, Morgan & Co., in partnership with Anthony Drexel, a Philadelphia banker. This firm was the U.S. branch of Drexel & Co., with close ties to J.S. Morgan & Co. in London (his father’s bank). Headquarters: New York City
Establishment of J.P. Morgan & Co. (1895)
Following the death of Anthony Drexel in 1893, the firm was reorganized and renamed: 1895: Drexel, Morgan & Co. became J.P. Morgan & Co. J.P. Morgan & Co. became one of the most influential and powerful private banks in the world.
What Made J.P. Morgan & Co. Powerful?
Industrial Financing. Financed and reorganized railroads like: New York Central. Erie Railroad. Northern Pacific. Backed Thomas Edison’s electric companies and helped merge them into General Electric in 1892. Financed and created U.S. Steel in 1901, the world’s first billion-dollar corporation.
Crisis Management. During the Panic of 1907, Morgan personally led a coalition of banks and trust companies to inject liquidity into the financial system — effectively acting as the central bank before the Federal Reserve existed (which was founded in 1913). He coordinated rescues of multiple institutions and is credited with preventing a complete collapse of the American banking system.
After J.P. Morgan's death in 1913: His son, J.P. Morgan Jr., took over leadership. The bank retained prominence but adapted to the rise of public capital markets and regulatory changes like the Glass-Steagall Act (1933), which required commercial and investment banking to be separated.
Today, J.P. Morgan’s name lives on in: J.P. Morgan (investment bank brand) – advisory, M&A, capital markets. JPMorgan Chase & Co. – the full multinational banking group. One of the world’s most respected financial institutions, with $4+ trillion in assets and operations in 100+ countries.
J.P. Morgan’s origins trace back to 1871, when it was founded as Drexel, Morgan & Co. The firm was later renamed J.P. Morgan & Co. and rose to prominence under the leadership of John Pierpont Morgan. During the early 20th century, J.P. Morgan helped finance and consolidate key U.S. industries, including railroads, steel, and electricity. He was instrumental in stabilizing financial markets during times of crisis, most notably the Panic of 1907.
In 2000, J.P. Morgan merged with Chase Manhattan Bank, forming JPMorgan Chase & Co., which has since become the largest bank in the U.S. by assets and market capitalization.
J.P. Morgan delivers a full suite of services across global financial markets. Its primary business units include:
Investment Banking. Mergers & acquisitions (M&A) advisory. Capital raising via equity and debt offerings. Strategic corporate finance. Initial Public Offerings (IPOs). J.P. Morgan consistently ranks among the top investment banks globally, acting as a trusted adviser to governments, large corporations, and institutions.
Markets & Securities Services. Sales and trading of equities, fixed income, currencies, and commodities. Prime brokerage and derivatives services. Custody and fund services. Market research and analytics.
Commercial Banking. Lending, credit, and treasury services for mid-sized and large businesses. Real estate financing. Industry-specific solutions (e.g., tech, healthcare, manufacturing).
Asset & Wealth Management. Investment strategies for institutions and high-net-worth individuals. Private banking and retirement solutions. ESG and sustainable investing portfolios. $3+ trillion in assets under management.
Treasury & Payments. Global payments and liquidity management. Trade finance and cross-border payments. Corporate treasury solutions through J.P. Morgan Payments.
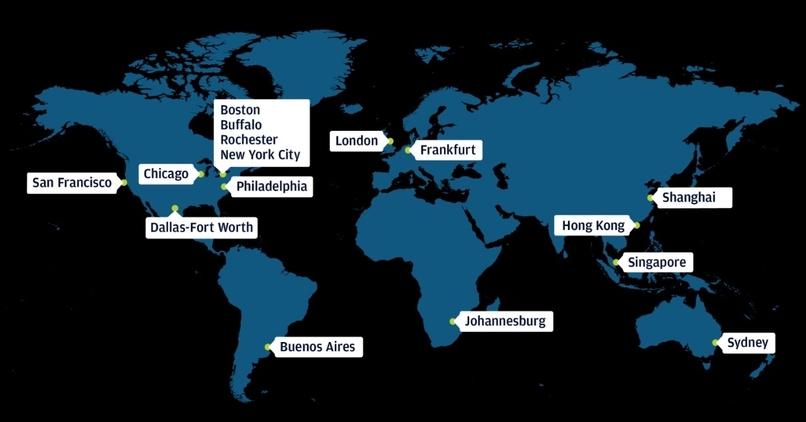
J.P. Morgan’s global operations span across: North America: U.S. headquarters in New York City, strong retail and investment operations. Europe: London regional headquarters and expanded post-Brexit EU banking hub in Frankfurt. Asia-Pacific: Major offices in Singapore, Hong Kong, Tokyo, and Mumbai. Latin America: São Paulo serves as the regional hub for capital markets and trade finance. Middle East & Africa: Growing presence in Dubai, Johannesburg, and Nairobi. With over 100,000 institutional clients, J.P. Morgan plays a vital role in supporting global commerce, government policy, and infrastructure development.
Though headquartered in New York City, JPMorgan Chase is truly a global financial institution, operating in more than 100 countries across North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East.
Clients include: Multinational corporations. Governments and central banks. Financial institutions. Small and mid-sized enterprises. High-net-worth individuals and retail customers. Its operations are supported by major offices in London, Hong Kong, Singapore, São Paulo, Frankfurt, Tokyo, and Dubai.
J.P. Morgan is not just a name; it is a symbol of financial power, global influence, and enduring legacy. From its 19th-century origins in the United States to its present status as a multinational banking giant, JPMorgan Chase & Co. has grown into the world’s most valuable bank by market capitalization, with operations in over 100 countries.
The origins of J.P. Morgan’s global legacy begin with John Pierpont Morgan, one of the most influential financiers in American history. In 1871, J.P. Morgan partnered with Anthony Drexel to establish Drexel, Morgan & Co., a New York-based investment banking firm. By 1895, after Drexel’s death, the firm was renamed J.P. Morgan & Co. The firm’s early international power was based on European connections, notably through his father’s London-based bank, J.S. Morgan & Co.
Morgan leveraged these ties to raise capital in London, Paris, and Berlin, making it possible to finance major U.S. infrastructure like railroads, steel, and electricity, as well as international bond offerings.
In the late 1800s and early 1900s, Morgan cemented his influence by: Financing and consolidating railroads that expanded U.S. trade routes and supply chains. Creating U.S. Steel, the first billion-dollar corporation. Merging Edison General Electric and Thomson-Houston to form General Electric. Bailing out the U.S. economy during the Panic of 1907, earning trust from global financial institutions
As American companies expanded abroad, J.P. Morgan followed, helping finance international expansion and managing cross-border transactions, making it an essential link between U.S. and European capital markets.

Over the 20th century, J.P. Morgan & Co. grew by adapting to international opportunities, but its global scale truly accelerated through strategic mergers.
2000: Merger of J.P. Morgan & Co. with Chase Manhattan Bank → Formed JPMorgan Chase & Co. Combined J.P. Morgan’s investment banking strength with Chase’s global retail and commercial banking network.
2004: Acquired Bank One Corporation. Brought in CEO Jamie Dimon and expanded into the Midwest and Southwest U.S.
2008: Amid the global financial crisis, JPMorgan Chase: Acquired Bear Stearns (boosting its investment banking arm). Acquired Washington Mutual, significantly expanding its U.S. retail presence.
These moves made JPMorgan Chase a financial superpower with global operations across all financial sectors: investment banking, consumer banking, asset management, and transaction services.
As banking evolved, so did JPMorgan Chase: It became one of the earliest adopters of technology to drive global scale and efficiency.
Today, it invests over $15 billion annually in: Artificial Intelligence (risk management, fraud detection, predictive analytics). Blockchain and digital assets (JPM Coin, Liink network). Cybersecurity and cloud infrastructure (critical for cross-border operations)
These investments allowed JPMorgan to offer real-time global payments, multi-currency clearing, and seamless international capital markets access, serving clients from New York to Nairobi.
JPMorgan Chase operates globally through local subsidiaries, joint ventures, and regional headquarters. Major international hubs: London (Europe HQ – investment banking, asset management). Hong Kong & Singapore (Asia-Pacific HQs). São Paulo, Brazil (Latin America regional base). Frankfurt (EU banking license post-Brexit). Tokyo, Dubai, Shanghai, and Mumbai (strategic financial centers).
Through these offices, J.P. Morgan offers services in: International M&A and IPOs. Global treasury and liquidity services. Securities and fund servicing for institutions. Private banking for high-net-worth individuals.
J.P. Morgan has earned the trust of: Sovereign governments (e.g., helping countries issue sovereign bonds). Multinational corporations (managing global payroll, FX, and investment). Central banks (clearing U.S. dollar payments, offering risk advisory). Large institutions (like pension funds, hedge funds, and asset managers). Its global network, liquidity, and reliability make it the go-to partner for large-scale international financial operations.
To solidify global dominance, J.P. Morgan: Hosts global investment forums (e.g., the Global China Summit, Global Markets Conference). Partners with fintech startups across Europe, India, and Southeast Asia. Serves as an adviser on global ESG investments, sustainable finance, and carbon market strategies. Is a thought leader in global macroeconomic analysis, publishing widely followed forecasts.
JPMorgan Chase extends its global footprint not just for profit but also through philanthropic and ESG-driven programs: Supports entrepreneurship and small business growth in Africa, Latin America, and Asia. Invests in inclusive hiring, education, and financial literacy. Promotes climate resilience projects and sustainable investing through global initiatives.
From a 19th-century financier to a 21st-century multinational banking juggernaut, J.P. Morgan’s journey to worldwide dominance has been defined by: Strategic foresight. Relentless innovation. Global ambition. Deep-rooted client trust. Today, JPMorgan Chase & Co. is more than a bank — it is a global financial ecosystem, powering businesses, governments, and economies worldwide.
Corporate & Investment Bank (CIB). One of the world's largest investment banks.
Core Services: M&A Advisory. Debt and Equity Capital Markets (IPOs, bond issuance). Sales & Trading: Fixed income, equities, commodities. Securities Services: Custody and fund services. Treasury Services: Cash management, payments, liquidity solutions.
Commercial Banking. Serves medium to large businesses, municipalities, and real estate developers. Products: Business loans and credit. Real estate financing. Treasury and payment solutions. Industry-specific financial advice (e.g., tech, healthcare)
Consumer & Community Banking (via Chase brand). Targeted at individuals and small businesses, primarily in the U.S. Products: Checking & savings accounts. Mortgages & auto loans. Credit cards (Chase Sapphire, Freedom, Amazon, Southwest Airlines, etc.). Mobile and digital banking via the Chase app. Wealth planning for mass affluent clients.
Asset & Wealth Management. Offers tailored investment and wealth solutions for individuals, family offices, and institutions. Services: Private banking. Investment advisory. Retirement planning (401k, IRAs). Alternative investments (hedge funds, private equity). Sustainable/ESG investing options
Financial Transaction Processing. JPMorgan is a leader in transaction services, processing trillions of dollars in daily payments through: Cross-border payments. Trade finance. Blockchain-based settlements (via JPM Coin and Liink platform). Real-time treasury and liquidity management tools. Its Onyx by J.P. Morgan division explores next-gen blockchain and digital asset solutions.
Philanthropic Initiatives and Social Responsibility
JPMorgan Chase is committed to inclusive economic growth through significant philanthropic investment and employee volunteerism.
Focus Areas: Workforce readiness: Training and upskilling underrepresented communities. Small business development: Grants, mentorship, and access to capital for minority- and women-owned businesses. Financial capability: Educational programs for budgeting, saving, and investing. Affordable housing: Investments in community development financial institutions (CDFIs). It has committed billions of dollars to racial equity and climate change initiatives globally.
New Headquarters: 270 Park Avenue, NYC. Under construction and scheduled for completion in November 2025. Will replace the old JPMorgan HQ. Designed as a sustainable, 60+ story skyscraper, setting new standards in green building technology.
Technological Advancements. Annual tech investment: ~$15 billion. Focus: AI, cybersecurity, mobile platforms, data analytics. JPM Coin pilot for blockchain-based settlement. AI-driven risk and fraud detection in digital banking
Reputation & Rankings
· Ranked #1 in global investment banking revenue
· One of Fortune's Most Admired Companies
· Leading ESG and diversity-focused employer
· Top retail bank in the U.S. by deposits
J.P. Morgan is one of the most tech-forward financial firms in the world, investing over $15 billion annually in technology. Innovations include: JPM Coin: A blockchain-based digital token used for real-time interbank settlements. Liink by Onyx: A blockchain-based data-sharing platform for global banks. AI and Data Analytics: Used in algorithmic trading, credit risk management, and fraud detection. Cybersecurity: Protecting billions of transactions across global networks.
Commitment to ESG and Social Impact. J.P. Morgan is committed to responsible banking and inclusive growth. Its key initiatives include: $30 Billion Racial Equity Commitment to advance homeownership, small business support, and financial literacy in underserved communities. Sustainable investing options and green bond underwriting. Investments in affordable housing, workforce training, and community development. Global volunteer programs and corporate philanthropy.
New Global Headquarters: A state-of-the-art skyscraper is under construction at 270 Park Avenue, NYC, scheduled for completion in November 2025. Expansion in Asia and Europe: Post-Brexit strategy has strengthened its EU presence via Frankfurt, while it continues to expand its influence in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Private Credit Growth: The firm is aggressively building its position in the growing global private credit market.
J.P. Morgan’s rise from a 19th-century merchant bank to a 21st-century global financial leader is a story of vision, innovation, and influence. Through strategic mergers, technological investment, and an unwavering commitment to client service, J.P. Morgan has solidified its position at the heart of the global economy.
As financial systems evolve, J.P. Morgan continues to lead, not only as a bank, but as a strategic partner, technological innovator, and global economic steward.